05 December, 2025
Choosing the right leather thickness can make or break your fashion accessory design. Whether you're crafting a sleek wallet or a sturdy belt, understanding the difference between thin and thick leather is essential for creating products that balance style, durability, and functionality.
Thin leather offers exceptional flexibility and a refined aesthetic, perfect for delicate accessories like clutches and cardholders. Thick leather, on the other hand, provides the structural integrity needed for heavy-duty items such as luggage and belts. As the fashion industry increasingly embraces synthetic leather and faux leather for their affordability, consistency, and sustainable production methods, designers have more options than ever to achieve their creative vision without compromising on quality.
Rock Uniquoters, a leading manufacturer of premium synthetic leather, understands these nuances and offers fashion brands innovative solutions tailored to diverse accessory requirements—from ultra-thin garment-weight materials to robust, heavy-duty options.
What Is Leather Thickness? Why It Matters
Leather thickness is typically measured in millimeters (mm) or ounces (oz), with 1 oz roughly equal to 0.4 mm. The thickness you choose determines how strong, flexible, and structured a final accessory will be.
A thinner material creates sleek, bendable designs, while thicker leather adds weight, stability, and long-term durability. Understanding leather thickness is essential for selecting the right material for each accessory type.
In this context, secondary keywords like leather thickness, leather thickness guide, and leather thickness chart fit naturally because thickness directly shapes product performance, comfort, and style outcomes.
Thin Leather: Features, Benefits, Limitations & Uses
What Qualifies as Thin Leather?
Thin leather especially thin synthetic or faux leather generally falls between 0.4 mm and 1.2 mm. This range is preferred for small, flexible, and lightweight fashion items.
Key Characteristics of Thin Synthetic Leather
-
Lightweight and easy to handle
-
Soft, smooth hand feel
-
Highly flexible
-
Ideal for intricate details
-
Comfortable against skin
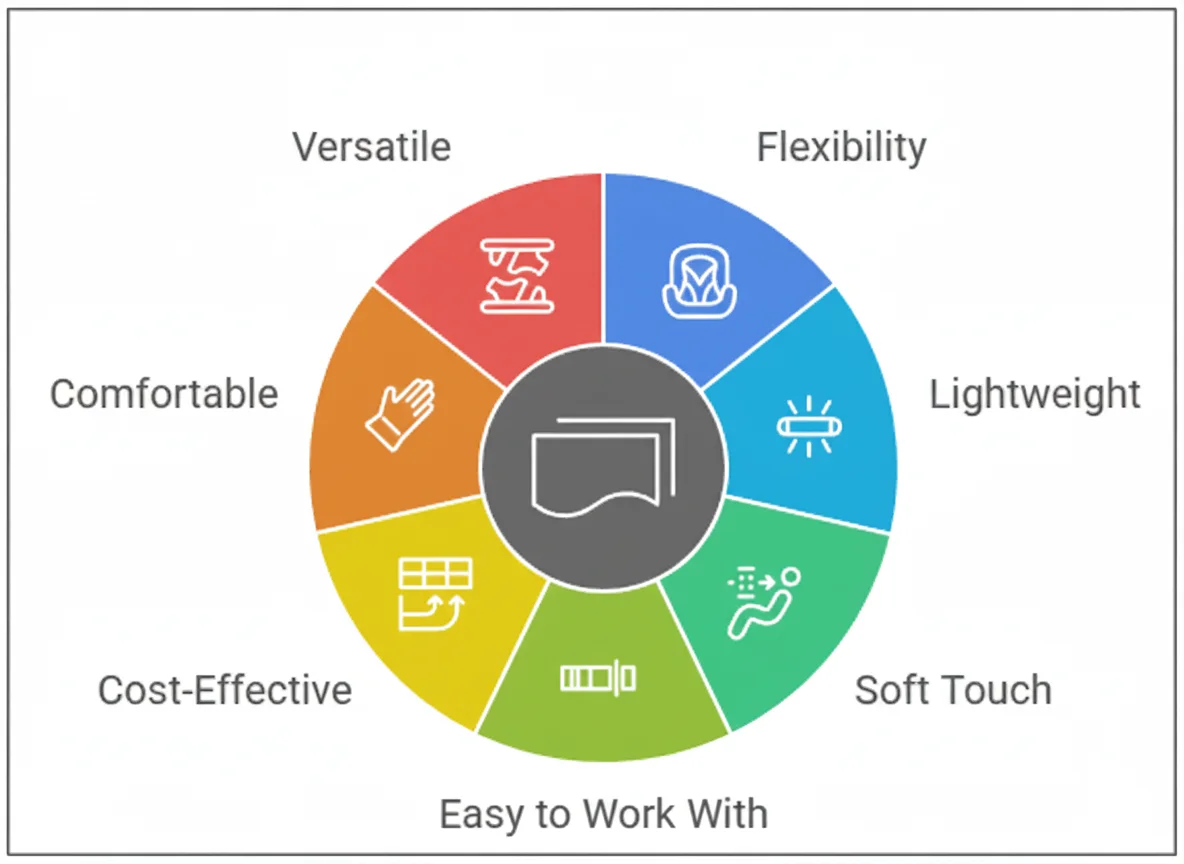
Advantages of Thin Leather
-
Flexibility: Perfect for designs requiring curves, folds, and soft silhouettes.
-
Lightweight: Makes accessories easy to carry and wear.
-
Soft Touch: Offers a luxurious feel without extra bulk.
-
Easy to Work With: Great for fine stitching and detailed craftsmanship.
-
Cost-Effective: Uses less material overall.
-
Comfortable: Works well for wearable accessories like gloves or straps.
-
Versatile: Supports embossing, prints, and modern design elements.
Limitations
-
Lower structural strength
-
Often needs a lining or reinforcement
-
Limited resistance to punctures
-
Can lose shape if overstretched
Best Applications for Thin Faux Leather
Fashion Accessories:
-
Wallets and slim cardholders
-
Clutches and evening bags
-
Gloves and watch straps
-
Small pouches and coin purses
-
Jacket trims and linings
-
Book covers
-
Phone cases and minimalistic sleeves
Thick Leather: Features, Benefits, Limitations & Uses
What Defines Thick Leather?
Thick leather typically ranges from 1.5 mm to 2.5 mm or more. Its density and rigidity make it ideal for heavy-duty, long-lasting products.
Key Characteristics of Thick Faux/Synthetic Leather
-
High durability
-
Strong structural base
-
Premium, weighty feel
-
Better resistance to scratches
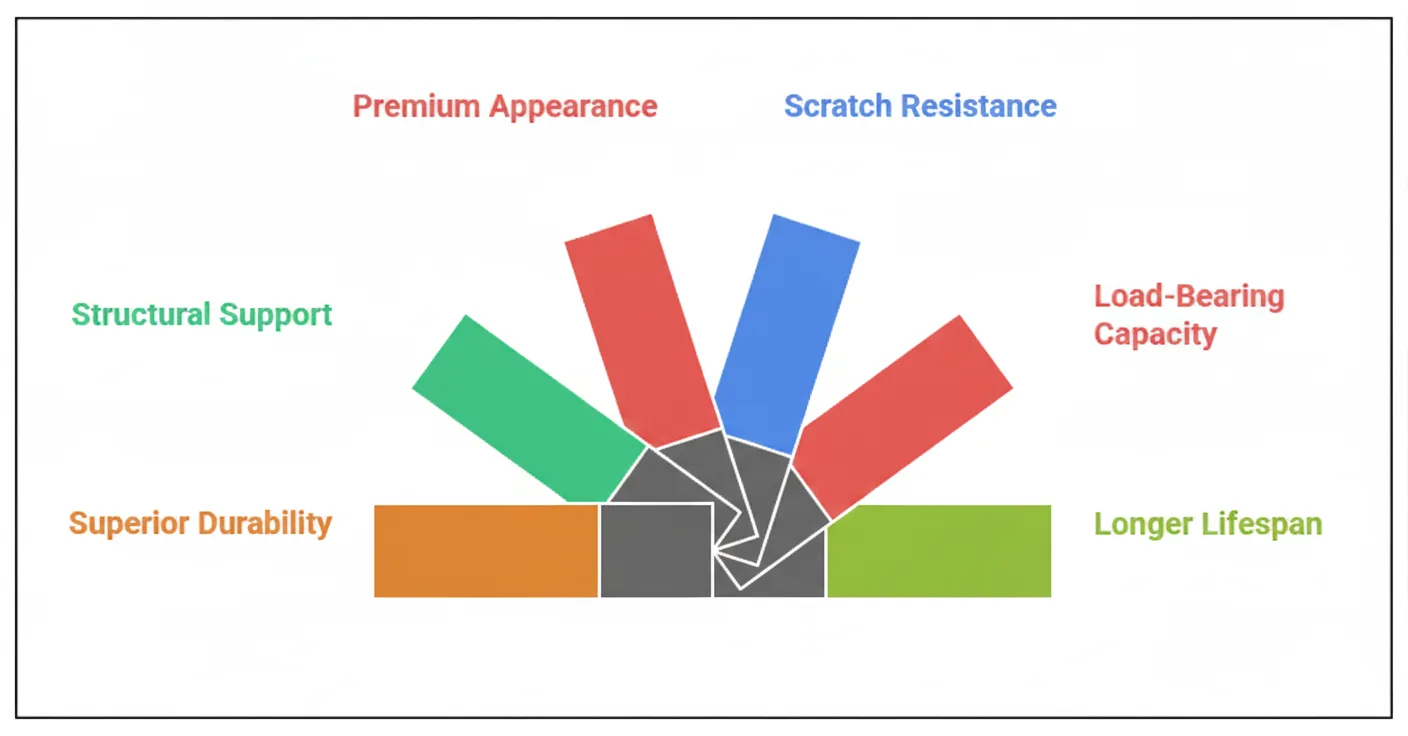
Advantages of Thick Leather
-
Superior Durability: Designed for daily or rugged use.
-
Structural Support: Retains shape without extra backing.
-
Premium Appearance: Heavier feel enhances perceived value.
-
Scratch Resistance: Protects surfaces better than thin variants.
-
Load-Bearing Capacity: Suitable for bags and straps that must carry weight.
-
Longer Lifespan: Less likely to warp or lose integrity over time.
Limitations
-
Heavier and less flexible
-
Difficult to shape for complex designs
-
Requires industrial machinery for cutting and stitching
-
Costs more per square meter
-
May feel stiff during initial use
Best Applications for Thick Faux Synthetic Leather
Heavy-Duty Accessories:
-
Leather belts (1.8–2.2 mm preferred)
-
Messenger bags, laptop bags, and briefcases
-
Travel bags and luggage
-
Large tote bags
-
Boot and work footwear
-
Backpack straps
-
Furniture & automotive interiors
-
Pet collars and leashes
Comparison Table: Thin vs Thick Leather for Accessories
| Feature | Thin Leather | Thick Leather |
|---|---|---|
| Flexibility | High | Moderate |
| Durability | Medium | High |
| Ideal Applications | Wallets, gloves, small goods | Bags, belts, straps |
| Appearance | Soft, sleek | Textured, premium |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavy & sturdy |
Here, the phrase leather thickness chart appears naturally because the table serves as a reference.
How to Choose the Right Thickness
Choosing between thin and thick materials becomes easier with a structured decision-making approach.
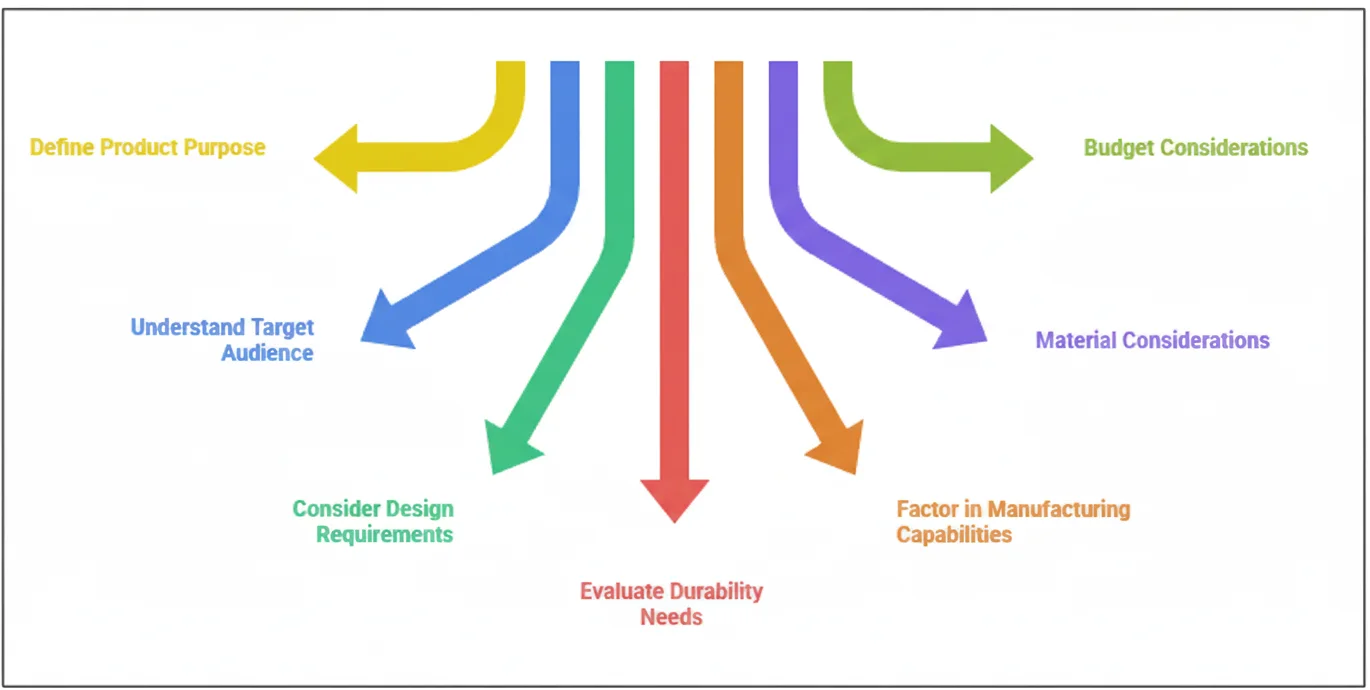
Step 1: Define Your Product’s Main Purpose
-
Is the accessory decorative, functional, or both?
-
Will it carry weight?
-
Should it be soft or structured?
Step 2: Understand Your Target Audience
-
Luxury buyers prefer structured, thick materials.
-
Budget-friendly markets benefit from cost-effective synthetic leather options.
-
Eco-conscious shoppers appreciate sustainable synthetic leather alternatives.
Step 3: Consider Design Requirements
-
Intricate patterns: thin material
-
Structured silhouettes: thicker material
-
Heavy hardware: thicker support base
Step 4: Evaluate Durability Needs
Durability Checklist:
-
High durability (belts, luggage): 1.8 mm+
-
Medium durability (daily handbags): 1.2–1.8 mm
-
Low-stress items (wallets): 0.8–1.2 mm
Step 5: Factor in Manufacturing Capabilities
-
Machinery limitations
-
Stitching strength
-
Production volume and speed
Step 6: Material Considerations
-
Faux leather composition (PU vs PVC)
-
Backing material strength
-
Type of surface finish
Step 7: Budget Considerations
-
Thicker leather costs more
-
Must consider cost per square foot
-
Balance price with product positioning
Testing Recommendations
-
Create prototypes in 2–3 thickness variations
-
Check stitching behavior, folding ability, and overall look
-
Gather user or client feedback
Leather Thickness Chart: Accessory-Specific Guide
| Fashion Accessory | Recommended Thickness | Why This Thickness? |
|---|---|---|
| Wallets | 0.8–1.2 mm | Slim, sleek, pocket-friendly |
| Small Handbags | 1.0–1.5 mm | Structure + flexibility |
| Large Handbags | 1.5–2.0 mm | Shape retention, weight support |
| Crossbody Bags | 1.2–1.6 mm | Comfortable for daily wear |
| Belts | 1.8–2.5 mm | Strong buckle support |
| Clutches | 0.6–1.0 mm | Lightweight elegance |
| Backpacks | 1.5–2.2 mm | Durability for daily use |
| Luggage | 2.0–2.8 mm | Heavy-duty protection |
| Watch Straps | 0.8–1.2 mm | Soft, flexible fit |
| Shoe Uppers | 1.0–1.5 mm | Breathable yet durable |
| Boots | 1.8–2.5 mm | Structure & weather resistance |
| Laptop Bags | 1.5–2.0 mm | Protection & professional look |
Use this chart as a starting guideline. Always confirm final thickness through prototyping.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Selecting Leather Thickness
Mistake 1: Choosing Thickness Based Solely on Price
The cheapest option often fails durability tests, leading to returns and damaged brand reputation. Calculate total cost of ownership, including potential replacements and customer service expenses.
Mistake 2: Ignoring End-Use Environment
Hot, humid climates require different specifications than cold, dry conditions. Leather thickness for bags used in tropical regions needs breathability considerations that temperate climate products don't.
Mistake 3: Not Testing Samples
Specifications on paper differ dramatically from physical reality. Always order actual samples before bulk purchases what looks perfect in a catalog might feel wrong in hand.
Mistake 4: Overlooking Hardware Compatibility
Thin leather cannot support heavy buckles, rivets, or snap closures without tearing. Match thickness to hardware weight and anticipated stress at attachment points.
Mistake 5: Assuming All Suppliers Have Same Standards
A "1.2mm" specification varies between manufacturers. Request actual measurements and acceptable tolerances to ensure consistency across orders.
Mistake 6: Not Accounting for Stretch and Wear
Leather changes with use some stretch, others compress. Consider how thickness affects long-term performance and factor in aging characteristics during design.
Why Fashion Brands Prefer Synthetic or Faux Leather Today
Modern fashion brands increasingly choose faux synthetic leather and other alternative materials because they offer consistency, sustainability, and versatility that natural leather cannot always match. Synthetic leather provides uniform thickness, smoother textures, and color accuracy qualities essential for mass production. It resists moisture, ages well, and is more cost-effective for brands targeting wider markets.
This material also aligns with growing eco-conscious consumer preferences, as many faux leather options reduce waste and animal-derived materials. With advancements in technology, today’s synthetic leather can mimic premium textures while offering better durability and design flexibility.
Rock Uniquoters supports this shift with innovative synthetic leather solutions that meet modern fashion standards for quality, performance, and style.
Expert Tips for Working With Thin & Thick Leather
-
Choose thickness based on product lifecycle and usage
-
Match stitching techniques and thread strength with material type
-
Ensure the surface finish complements your accessory aesthetic
-
Use thicker material for structure, thinner for premium flexibility
-
Choose faux leather when consistency and cost control matter
-
Test hardware compatibility before finalizing your design
Conclusion
Both thin and thick leather play crucial roles in fashion accessory design. Thin leather offers softness, flexibility, and lightweight comfort, while thick leather delivers strength, durability, and long-lasting structure. With growing interest in synthetic leather and faux leather, brands now have reliable, consistent alternatives for modern manufacturing needs.
Rock Uniquoters continues to lead the industry by providing high-quality synthetic leather materials tailored for fashion, accessories, and lifestyle products.
Choosing the right thickness ensures your accessory performs beautifully while maintaining the desired style and comfort. Always balance function, aesthetics, and target audience expectations when selecting materials.
FAQs
1. Is thin or thick leather better for handbags?
Thin leather works well for lightweight, soft handbags, while thick leather provides structure and long-term durability. For everyday handbags, designers often choose medium thickness (1.2–1.8 mm) to balance comfort, strength, and aesthetics.
2. What is the ideal leather thickness for belts?
Belts require strong, rigid material that can withstand buckle pressure. The ideal thickness is between 1.8 mm and 2.5 mm, depending on whether the belt is for fashion, formal wear, or heavy-duty use.
3. Is synthetic leather as durable as real leather?
High-quality synthetic leather is engineered for strength, flexibility, and resistance to cracking. While it behaves differently than natural leather, modern synthetic variants often outperform real leather in moisture resistance, uniformity, and long-term wear.
4. How do I check leather thickness?
Leather thickness is measured using a gauge or caliper in millimeters. For accuracy, check multiple points across the surface. Most suppliers also provide a measurement sheet or tolerance chart for quality assurance.
5. Does thick faux leather crack over time?
Thick faux leather does not usually crack if it’s high quality and maintained properly. Cracking typically occurs due to poor material composition, extreme heat, or lack of flexibility in the product design.
6. Is thin leather good for wallets and small accessories?
Yes, thin leather between 0.8 mm and 1.2 mm is ideal for wallets, cardholders, and small accessories. It offers the right balance of flexibility, comfort, and slim design without adding unnecessary bulk.



